What is cloud computing?
The e-commerce industry benefits small and medium businesses that need a wider reach. Technology boosts businesses in this digital age. It is not surprising that more entrepreneurs want to learn more about it. The latest practical means of an online venture is cloud computing.
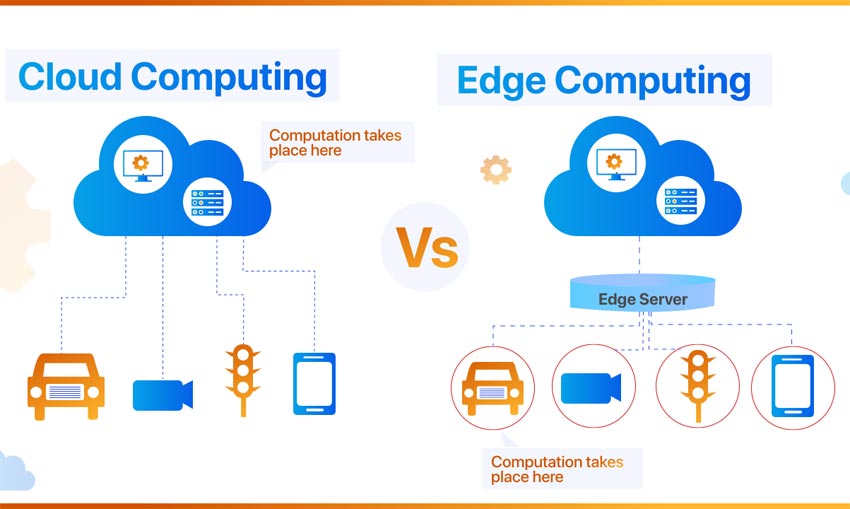
Cloud computing is a network of servers connected using the Internet. Its primary function is to share information, resources, and software. Cloud computing is a popular practice involving the internet to store and manage your data on the internet, the Internet acts as the invisible cable that connects everything. This includes all physical and virtual servers all over the globe. There are many free online cloud computing courses available to begin with basic understanding of it.
You Can Also Read: Common Use of AI in Modern Knowledge Management
How does it work-
The cloud computing section is divided into two: the front end and the back end. The front end is the side where clients access the Internet for data. This includes computers, computer networks, applications, and all means for clients to access the cloud computing system.
The back end consists of all things needed for cloud computing services. This is the side of the cloud computing provider. This includes servers, computers, data storage systems, programs, and all necessary means to provide different cloud computing services.
Cloud computing services accelerate Big Data and business intelligence computing operations, enable software modernization through micro services, and are vital for an e-commerce software engine. It results in streamlining and simplifying business applications, fastening time to market, and meeting customer demands effectively.
What is edge computing?
Edge computing is a “mesh network of micro data centers that process or store critical data locally and push all received data to a central data center or cloud storage repository, in a footprint of less than 100 square feet,” according to research firm IDC. It is typically referred to in to use cases, where edge devices would collect data – sometimes massive amounts of it – and send it all to a data center or cloud for processing. Edge computing triages the data locally so some of it is processed locally, reducing the backhaul traffic to the central repository.
Examples of edge computing use cases include industrial sensors monitoring factory machines, devices to measure soil moisture in agriculture fields, and the information processing done by self-driving cars. Across all of these devices, edge computing makes it possible to process and act on local data in near real-time. Devices used for edge computing can be as simple as a Raspberry Pi server or as complex as an AI system with FPGA or CPU hardware—the key characteristic is that the computing is done at or near where data is generated in a standalone device or small cluster (as opposed to a full, racked data center).
Speed is no longer just a competitive advantage, it's a best practice. The most important advantage of peripheral computing is its ability to increase network performance by reducing latency. By processing data closer to the source and reducing the physical distance to travel, peripheral computing can significantly reduce latency. On-premises devices can summarize or encrypt the data that needs to be sent and retrieved from the cloud to allow much smaller packets to be sent to the cloud.
The most important advantage of peripheral computing is its ability to increase network performance by reducing latency. Since IoT edge computing devices process data locally or in nearby edge data centers, the information they collect should not go nearly as far as in traditional cloud architecture.
Advantages of Using Cloud Computing Services:
1) High Speed:
Developers can easily test new ideas and design application architecture without the dependency on on-site hardware limitations or slow procurement processes.
2) Data Security:
Cloud offers many advanced security features that guarantee that data is securely stored and handled. Cloud storage providers implement baseline protections for their platforms and the data they process, such as authentication, access control, and encryption. From there, most enterprises supplement these protections with added security measures of their own to bolster cloud data protection and tighten access to sensitive information in the cloud.
3) Efficiency & Cost Reduction:
By using cloud infrastructure, you don’t have to spend huge amounts of money on purchasing and maintaining equipment. This drastically reduces the Cost of Ownership. You don’t have to invest in hardware, facilities, utilities, or building out a large data center to grow your business.
4) Storage Capacity:
The cloud has essentially unlimited capacity to store any type of data in various cloud data storage types, depending on the availability, performance and frequency the data has to be accessed. Creating and optimizing the cloud cost structure policy can reduce the cost of cloud storage significantly while maintaining the company’s business goals related to data storage in the cloud.
5) All over Functioning:
Cloud computing offers another advantage of working from anywhere across the globe, as long as you have an Internet connection.
6)24X7 Availability:
Most of the cloud providers are truly reliable in offering their services with most of them maintaining uptime of 99.9%.
Benefits of Edge Computing
1. Speed and Latency: The more time it takes to process data, the less useful it becomes. Time is of the essence in the case of the autonomous car, because most of the data it collects and requires becomes obsolete after a few seconds. On a congested highway, milliseconds are crucial. In the digital factory, where intelligence-based technologies constantly monitor all parts of the manufacturing process to maintain data consistency, milliseconds are also important. In many circumstances, there isn't enough time to round trip data between clouds.
2. Security: Because company devices are increasingly transferred outside of the protected firewall perimeter of the corporation, the advent of mobile computing has left businesses much more exposed. When data is evaluated locally, it is protected by the on-premise enterprise's security blanket. Edge computing also aids businesses in overcoming local compliance and privacy restrictions, as well as data sovereignty concerns.
3. Cost Savings: From a management standpoint, Edge Computing helps you to categorize your data. By storing as much data as possible in your edge locations, you may limit the amount of bandwidth required to connect all of your locations, and bandwidth costs money. Edge computing isn't about doing away with the cloud; it's about maximizing your operating costs by optimizing the flow of your data. Edge computing also helps to reduce data redundancy to some extent. At the very least, data created at the edge must be temporarily held there. It must be stored again after being sent to the cloud, resulting in levels of redundancy. When redundant storage is reduced, redundant costs are reduced.
4. Greater Reliability: In the world of IoT, there are some rather remote territories comprised of rural and less-than-ideal internet access situations. Reliability improves when edge devices can store and process data locally. Prefabricated mini data centers are now available that can operate in almost any environment. This means that smart device operations will not be impacted by temporary interruptions in intermittent connectivity simply because they have lost access to the cloud. Furthermore, each website has a built-in limit on the quantity of data that can be transmitted at any one time.
5. Scalability: Although it may appear counterintuitive to popular belief, the idea that edge computing provides a scaling benefit makes sense. In most circumstances, data must initially be routed to a centrally centralized data center, even in cloud computing infrastructures. Expansion or even simple modifications to specialized data centers are costly. Furthermore, rather than relying on the coordination of efforts from employees at numerous locations, IoT devices can be installed along with their processing and data management capabilities at the edge in single implantation.
Who wins the race?
Edge and cloud computing have distinct features and most organizations will end up using both, a quick comparison can help:
In cloud computing, there is a reliable internet connection, whereas in edge computing Remote locations with limited or no internet connectivity
In cloud computing Non-time-sensitive data processing is being done, whereas in edge computing Real-time data processing is done
In cloud computing, there are dynamic workloads, whereas in edge computing there Large datasets that are too costly to send to the cloud
In cloud computing Data is stored in the cloud, whereas in edge computing there is highly sensitive data and strict data laws.
An example of a situation where edge computing is preferable over cloud computing is medical robotics, where surgeons need access to real-time data. These systems incorporate a great deal of software that could be executed in the cloud, but the smart analytics and robotic controls increasingly found in operating rooms cannot tolerate latency, network reliability issues or bandwidth constraints. In this example, edge computing offers life-or-death benefits to the patient.